I/O - File 클래스
java.io.File 클래스는 파일의 크기, 파일의 접근 권한, 파일의 삭제, 이름 변경 등의 작업을 할 수 있는 기능을 제공해 준다. (디렉토리도 파일 취급) 하지만, 파일 인스턴스를 만들었다고 해서 실제 폴더에 파일이 생성되는 것은 아니다.
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/17/docs/api/java.base/java/io/File.html
File (Java SE 17 & JDK 17)
All Implemented Interfaces: Serializable, Comparable An abstract representation of file and directory pathnames. User interfaces and operating systems use system-dependent pathname strings to name files and directories. This class presents an abstract, sys
docs.oracle.com
파일 정보를 자바에서 다음과 같이 알아낼 수 있다.
package theory.io;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.out.println("사용법 : java FileInfo 파일이름");
System.exit(0);
}
// File(String pathName)
File file = new File(args[0]);
if (file.exists()) { // 파일이 존재할 경우
System.out.println("file.length() = " + file.length());
System.out.println("file.canRead() = " + file.canRead());
System.out.println("file.canWrite() = " + file.canWrite());
System.out.println("file.getAbsolutePath() = " + file.getAbsolutePath());
try {
System.out.println("file.getCanonicalPath() = " + file.getCanonicalPath());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("file.getName() = " + file.getName());
System.out.println("file.getParent() = " + file.getParent());
System.out.println("file.getPath() = " + file.getPath());
} else {
System.out.println("파일이 존재하지 않습니다.");
}
}
}
다음은 파일 삭제와 관련된 코드이다.
package theory.io;
import java.io.File;
public class FileDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.out.println("사용법 : java FileDelete 파일이름");
System.exit(0);
}
File file = new File(args[0]);
if (file.exists()) {
boolean deleteFlag = file.delete();
if (deleteFlag) {
System.out.println("파일 삭제 성공!!");
} else {
System.out.println("파일 삭제 실패ㅠㅜ");
}
} else {
System.out.println("파일이 존재하지 않습니다.");
}
}
}
다음은 폴더의 리스팅 관련 코드이다.
package theory.io;
import java.io.File;
public class FileList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("/tmp/");
printFiles(file);
}
private static void printFiles(File file) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
if (f.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("[dir] f.getName() = " + f.getName());
printFiles(f);
continue;
}
System.out.println("f.getName() = " + f.getName());
}
} else {
System.out.println("디렉토리가 아닙니다.");
}
}
}
다음음 File 클래스를 이용한 임시 파일의 생성과 삭제 관련 코드이다.
package theory.io;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
// 임시 파일의 생성과 삭제
public class TempFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File f = File.createTempFile("tmp_", ".dat");
System.out.println("f.getAbsolutePath() = " + f.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("10초 동안 멈춰있다.");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000); // 10초 동안 프로그램이 멈춘다.
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
f.deleteOnExit(); // JVM이 종료될 때 임시파일을 자동으로 삭제한다.
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
ByteStream
Byte 단위로 입출력하는 클래스의 경우 모두 InputStream, OutputStream의 자식이다.
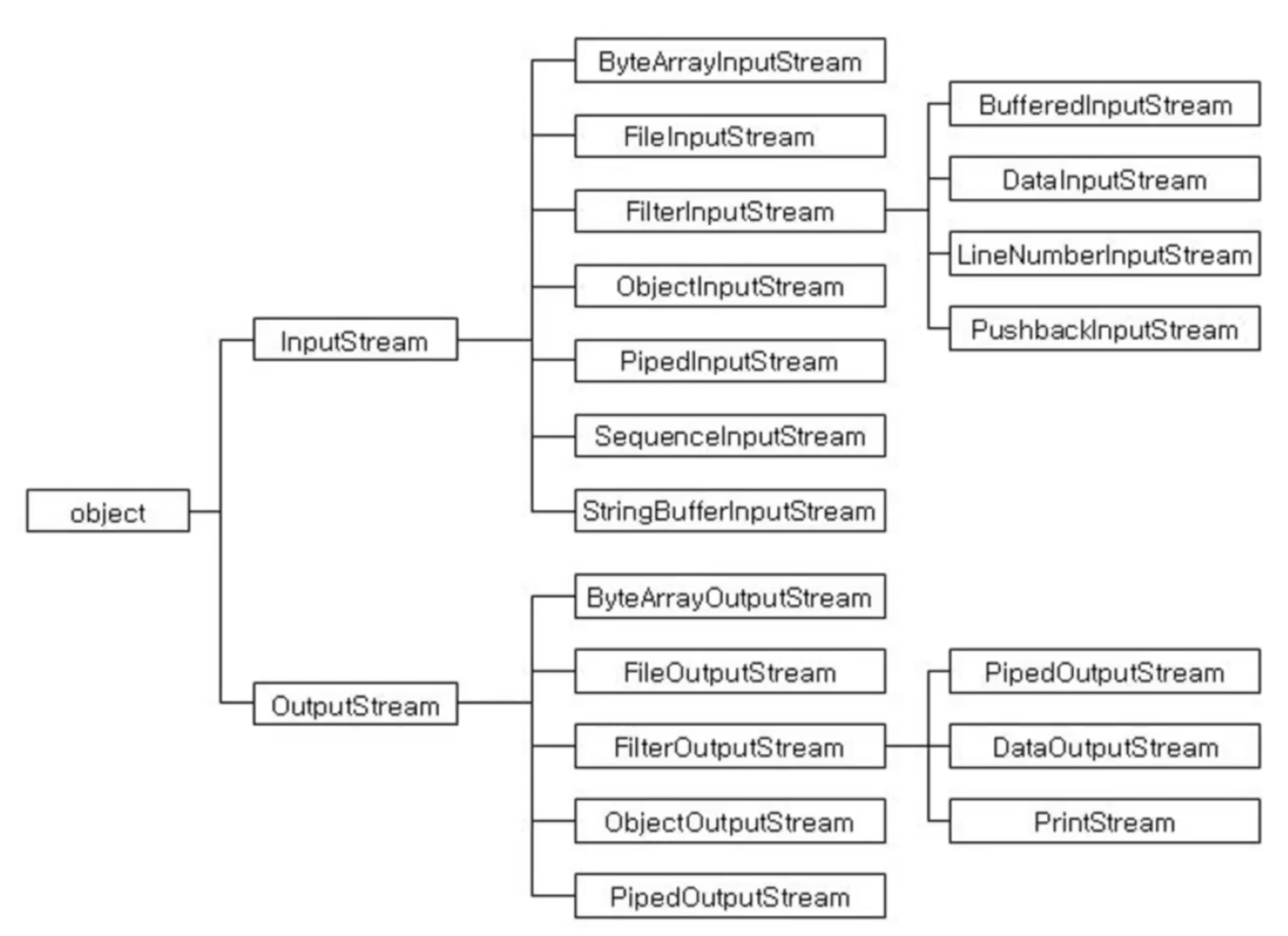
InputStream, OutputStream
추상클래스로써 byte 단위의 입출력 클래스는 이 클래스들의 후손이다.
왜 byte단위를 읽어들이는 read()는 int를 반환하게 되었을까?
다음 코드를 보면 inputStream.read()는 byte를 읽어들이므로 byte를 반환해야 할 것 같은데 int 값을 반환한다. 이때,
1byte가 표현할 수 있는 값은 00000000 ~ 11111111까지 있다. 즉, read()가 읽어들일 수 있는 정보는 저 값들 중에서 하나일 것이다.
즉, 1byte씩 파일을 읽어들인다. 그런데 파일의 크기를 모르면 언제까지 읽어들일까? 정답은 더이상 읽어들일 것이 없을 때까지이다. (EOF). 그리고 EOF는 00000000 ~ 11111111 사이의 값들로 표현할 수 없다는 소리이다.
그래서 1byte를 읽어들이지만 int에 1byte값을 담자고 자바 개발자들은 생각하게 되었다. (그릇을 큰걸 쓰자.)
즉, 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ~
00000000 00000000 00000000 11111111 처럼
4 byte 정수를 사용하는데, 맨 마지막 byte에 값을 담아서 반환하자고 생각한 것이다.
그리고 EOF는 -1로 나타내게 되었다. 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111
즉, 현재 단락에 대한 대답은 EOF를 표현할 수 있는 방법이 없어서이다.
package theory.io;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class InputStreamExam01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
int data = inputStream.read(); // byte -> int ?
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("io오류 = " + e);
} finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("io오류2 = " + e);
}
}
}
}
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/index.html?java/io/package-summary.html
Java Platform SE 8
docs.oracle.com
주인공을 찾는 문제
- 키보드로부터 한 줄씩 입력받아 화면에 출력
- txt 파일로부터 한 줄씩 입력받아 화면에 출력
- 키보드로부터 한 줄씩 입력받아 파일에 출력 (파일은 아규먼트로 받아들임)
- txt 파일로부터 한 줄씩 입력받아 다른 파일에 한줄씩 출력
인용